Need a nonstandard resistor value? This tool finds series and parallel pairs of standard values that approximate your desired value. To get started, enter your desired value in the target resistance field below.
This calculator finds pairs of series and parallel standard resistors to approximate a given value. It is useful for synthesizing non-standard or less common resistor values. Several results are provided, and are ranked by error.
Enter your desired target resistance value in the Target Resistance field. Select the desired scale (Ω, kΩ, or MΩ) using the menu on the right side of the input field.
Select the resistor series that you would like to use from the Resistor Series menu. Note that the series values represent standard E series values used by resistor manufacturers – for instance 1% resistors are typically available in the E96 series of values.
The results will show in a table, with a separate solution in each row. For each solution, the two standard resistors (R1 and R2) are given. The type of combination, series or parallel is shown. Their combined series or parallel resistance is shown, along with the error as compared to your target value. The results are sorted from least to greatest error.
Let's suppose that you need precision 0.1% tolerance resistor with a value of 1.571kΩ. First, check to see if there’s a matching standard value. You can use the Closest Standard Resistor calculator to do so:
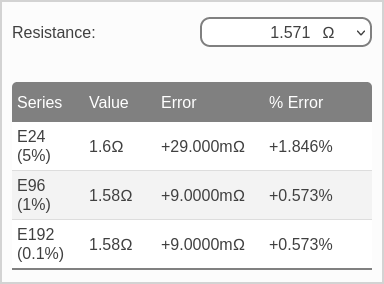
As the results show, the closes standard resistor is 1.58kΩ, with an error of +0.573%. This isn’t great, with the error exceeding the resistor tolerance by almost six times.
So, lets try the Series & Parallel Combination Calculator to see if we can do better. Start by entering 1.571kΩ in the Target Resistance field. Since many 0.1% resistors are available only in the E96 or 1% series of values, we’ll want to select E96 (1%) in the Resistor Series menu to to ensure easy to find components. The results will appear immediately:
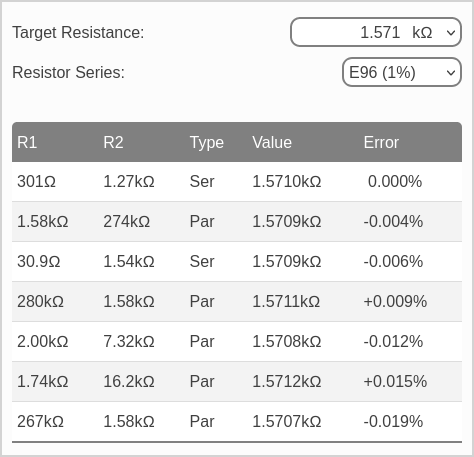
Each solution is shown in its own row. They are sorted by error from best to worst. Let's take a look at the best solution appearing in the first row. The first two columns, R1 and R2, provide the resistor pair values of 301Ω and 1.27kΩ. The next column, Type, indicates whether R1 and R2 are in series or parallel. In this case, the resistors are in series, indicated by Ser. The resulting series value is shown in the Value column as 1.5710kΩ, matching our target goal. Since this solution is exact, the error given in the final column is 0%.
The next best solution appears in the second row. This result is the parallel combination of 1.58kΩ and 274kΩ. The resulting parallel value of this pair is 1.5709kΩ.
Resistors are manufactured in limited sets of standard values based on the so called E-series standard numbers. For precision resistors, such as 0.1% tolerance, the available values are spaced in much larger increments than the resistor tolerance. For instance, most 0.1% resistors are available only in the E96 series, with values spaced about 2.5% apart. Thus there are large gaps between the standard values which are not available. These non-standard values can often be synthesized using a series or parallel pair of standard resistors.
Its often convenient to reduce the number of unique parts in a design. One strategy is sticking to a smaller E series, such as E24 and use series and parallel combinations to generate values not in the series.
If you're prototyping in the lab and need a resistor value that's not available, you can combine resistors that you do have in stock to generate your needed value.